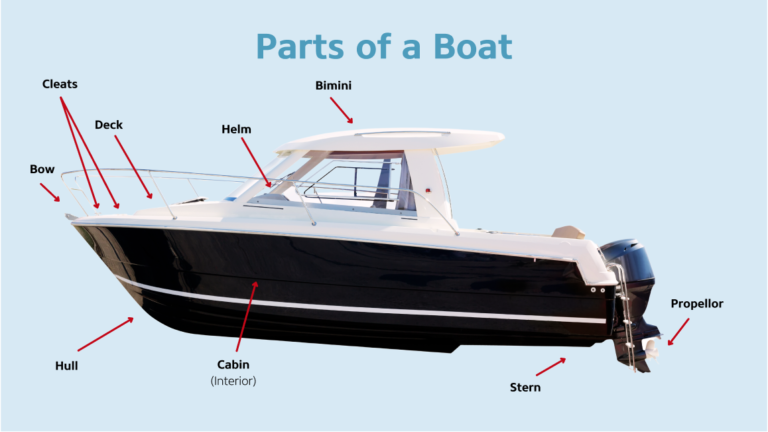
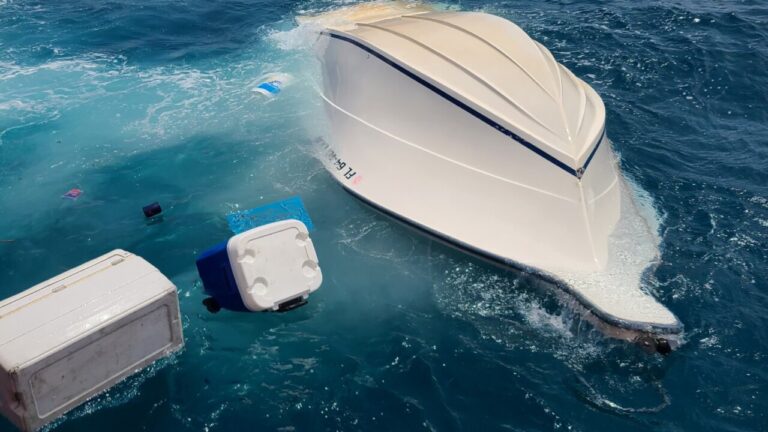
Recreational boating is a popular activity enjoyed by millions worldwide. While it offers great fun and relaxation, it also comes with inherent risks. On average, there are 4,000 non-fatal boating-related accidents and 500 fatal boating accident victims every year in the US alone. Understanding the primary causes of boating fatalities and how to prevent them is crucial for ensuring safety on the water. This comprehensive guide will delve into the main reasons behind boating accidents and provide actionable tips to avoid them.
The Causes and Prevention of Boating Fatalities
1. Lack of Proper Safety Equipment
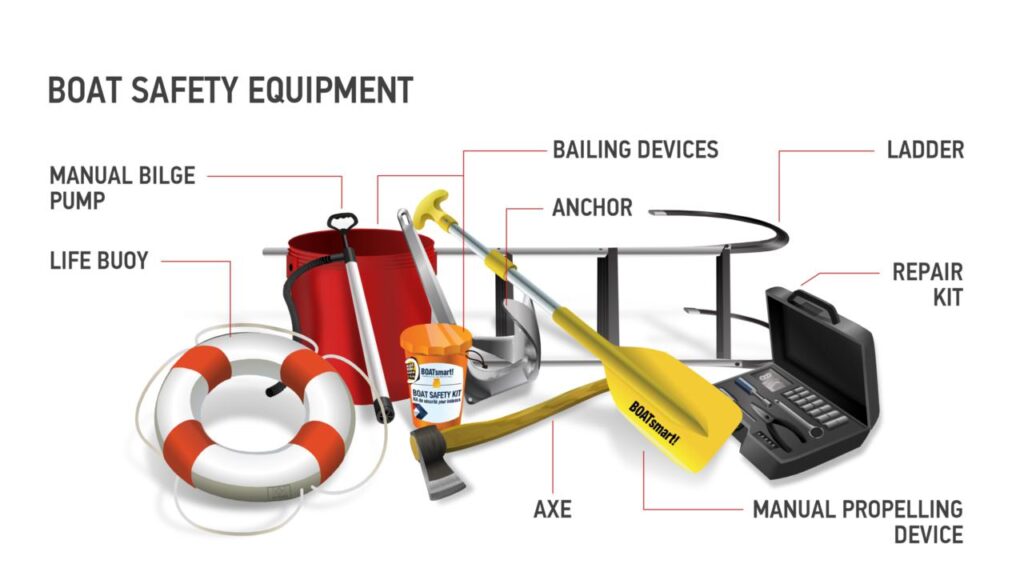
Causes
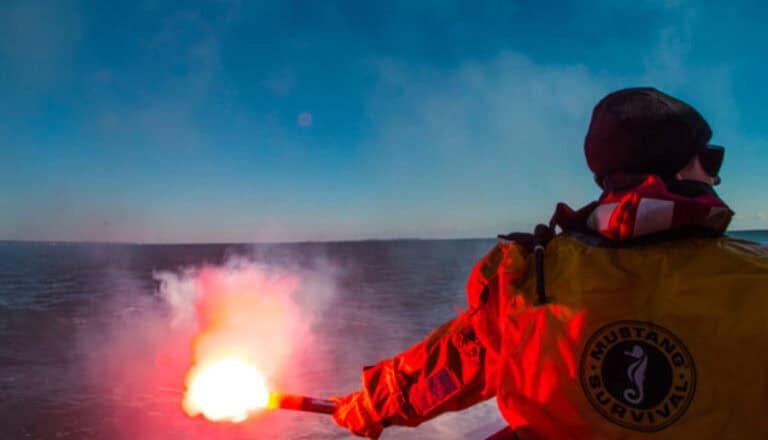
One of the leading causes of boating fatalities is the lack of proper safety equipment. Many boaters either do not have the necessary safety gear or fail to use it correctly. Essential safety equipment includes life jackets, fire extinguishers, distress signals, and first aid kits.
Prevention
- Life Jackets: Always wear a life jacket and ensure that all passengers do the same. The U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) reports that 84% of drowning victims in boating accidents were not wearing life jackets.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect safety equipment to ensure it is in good working condition.
- Education: Educate yourself on how to use safety equipment properly and provide boating safety instruction to your passengers.
Importance of Safety Equipment
Having the proper safety equipment on board can mean the difference between life and death. Life jackets, for instance, keep individuals afloat and reduce the risk of drowning, while fire extinguishers can prevent small fires from becoming catastrophic. Distress signals help rescuers locate a boat in trouble, and a well-stocked first aid kit can address injuries until professional help arrives.
2. Operator Inattention and Inexperience

Causes
Operator inexperience and inattention are primary contributing factors to boating accidents. Inattentive operators will maintain an improper lookout and may fail to notice hazards or react appropriately to changing conditions. Put down your phone! Inexperienced boaters might not understand the rules of the water or how to handle emergency situations.
Prevention
- Boating Courses: Take a boating safety course. Many organizations, such as the US Coast Guard Auxiliary and the American Boating Association, offer courses to enhance your skills and knowledge.
- Stay Alert: Always stay vigilant and pay attention to your surroundings, including other vessels, swimmers, and potential hazards.
- Limit Distractions: Minimize distractions such as mobile phones, loud music, or alcohol consumption while operating the boat.
Enhancing Experience and Attention
Continuous learning and practice can improve a boater’s experience and attentiveness. Regularly participating in boating activities and familiarizing oneself with different water conditions can help operators become more adept and responsive.
3. Alcohol Use

Causes
Alcohol consumption, behind the wheel of the boat, is another leading known contributing factor to boating fatalities. Alcohol use significantly impairs judgment, coordination, and reaction times, making it a leading cause of boating accidents. According to the United States Coast Guard, alcohol is the leading contributing factor in fatal boating accidents, accounting for nearly a quarter of all boating-related deaths.
Prevention
- Designate a Sober Operator: Always have a designated sober operator who abstains from alcohol while boating.
- Educate Passengers: Ensure that all passengers understand the dangers of alcohol consumption on the water.
- Strict Policies: Implement and enforce strict no-alcohol policies on your boat and keep each other accountable.
Impact of Alcohol on Boating
Alcohol impairs the body’s ability to regulate heat, increasing the risk of hypothermia even in moderately cool water. Additionally, alcohol reduces a person’s ability to swim and increases the chances of drowning if someone falls overboard.
4. Speeding

Causes
Operating a boat at an excessive speed reduces the operator’s reaction time and increases the severity of collisions. Speeding is particularly dangerous in congested areas, near shorelines, and in poor visibility conditions. Common vessel types involved are personal watercraft and racing boats.
Prevention
- Adhere to Speed Limits: Always follow posted speed limits and adjust your speed according to the conditions.
- Slow Down in Hazardous Areas: Reduce speed in congested areas, near docks, and in no-wake zones.
- Safe Speed Practices: Practice safe speed habits and maintain a speed that allows you to react quickly to any potential hazards.
Speed and Safety
Understanding the relationship between speed and safe navigation is crucial. Slowing down in high-traffic areas and when visibility is low ensures that the operator can respond effectively to unexpected situations, thereby preventing accidents.
5. Weather Conditions

Causes
Sudden changes in weather can catch boaters off guard, leading to dangerous situations. High winds, rough waters, and storms can all contribute to accidents and fatalities.
Prevention
- Check Weather Forecasts: Always check the weather forecast before heading out. Use reliable sources such as the National Weather Service.
- Weather Monitoring Devices: Equip your boat with weather monitoring devices and stay updated on changing conditions.
- Know When to Head Back: If you notice signs of deteriorating weather, head back to shore immediately.
Navigating Weather Risks
Understanding how to read the weather and recognize early signs of danger can prevent many weather-related accidents. Boaters should learn how to interpret weather patterns and signals, such as cloud formations and wind shifts, to make informed decisions while on the water.
6. Poor Maintenance and Mechanical Failures

Causes
Mechanical failures due to poor maintenance can lead to accidents and fatalities. Issues such as engine failure, steering problems, and fuel leaks can all create hazardous situations on the water.
Prevention
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance checks on your boat, including the engine, fuel system, and electrical components.
- Professional Inspections: Have your boat inspected by a professional at least once a year.
- Emergency Kits: Carry a well-stocked emergency repair kit to address minor issues on the water.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance not only ensures the longevity of your boat but also enhances safety. Keeping a detailed maintenance log can help identify patterns and predict when parts might need replacing, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
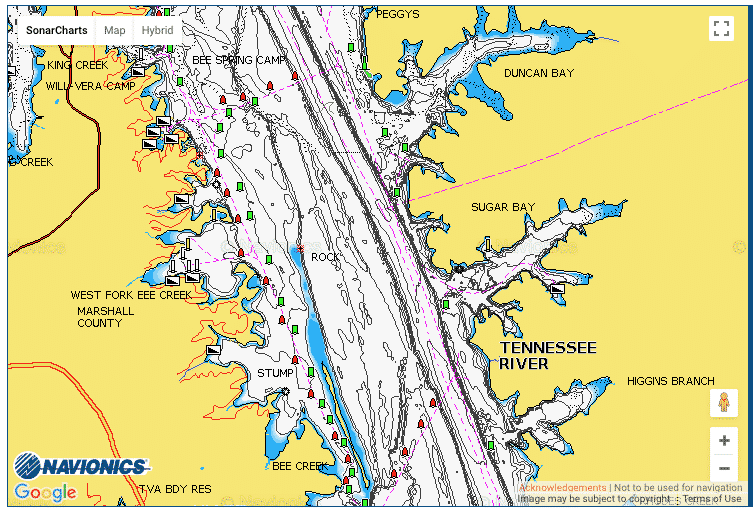
7. Navigational Errors
Causes
Navigational errors, such as failing to follow marked channels or not understanding navigational aids, can lead to collisions and groundings. Inadequate knowledge of the waterway can also result in dangerous situations.
Prevention
- Learn to Navigate: Take a navigation course to understand how to read charts and use navigational aids.
- Use GPS and Charts: Equip your boat with a reliable GPS and up-to-date charts.
- Plan Your Route: Plan your route in advance and familiarize yourself with the area, including potential hazards and landmarks.
Safe Navigation Practices
Developing good navigation habits, such as regularly checking position and speed, understanding tide schedules, and recognizing navigation markers, helps prevent errors that can lead to accidents.
8. Overloading and Improper Loading

Causes
Overloading a boat or improper weight distribution can affect stability and increase the risk of capsizing. Many boaters underestimate the importance of weight limits and balance.
Prevention
- Know Your Limits: Adhere to the manufacturer’s weight capacity and passenger limits.
- Even Distribution: Distribute weight evenly across the boat to maintain stability.
- Check Load Regularly: Regularly check the load and make adjustments as needed to ensure balance.
Understanding Capacity
Boaters should familiarize themselves with their vessel’s capacity plate, which indicates the maximum number of passengers and amount of weight the boat can safely carry. Adhering to these limits is essential for maintaining stability and safety.
9. Environmental Factors
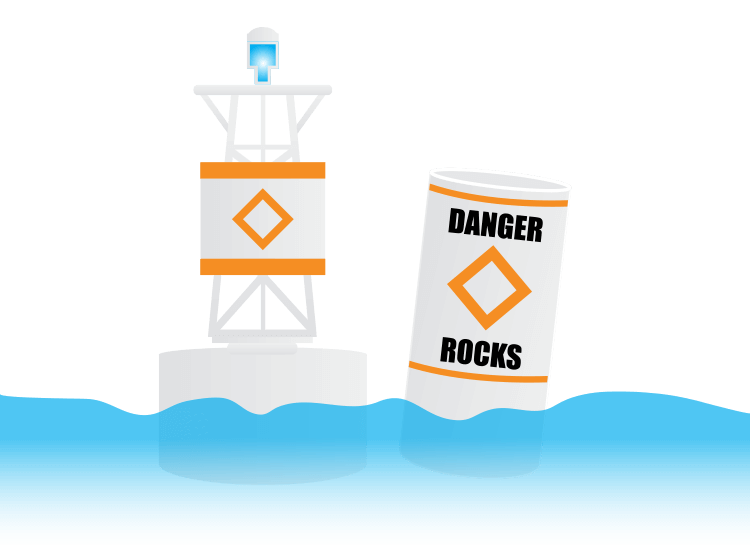
Causes
Environmental factors such as submerged objects, marine life, and strong currents can pose risks to boaters. These factors are often unpredictable and require constant vigilance.
Prevention
- Stay Informed: Familiarize yourself with the local waterway and any known hazards.
- Use Sonar: Equip your boat with sonar or fish-finding equipment to detect submerged objects.
- Be Cautious: Exercise caution when navigating unfamiliar areas or areas known for strong currents and marine life.
Adapting to the Environment
Understanding and adapting to the local environment is key to safe boating. Regularly updating your knowledge of the area, including any new hazards that may have developed, ensures preparedness and enhances safety.
10. Lack of Emergency Preparedness

Causes
Many boating fatalities occur because boaters are unprepared for emergencies. This includes not having a plan, inadequate first aid knowledge, and lack of communication equipment.
Prevention
- Emergency Plans: Develop and practice emergency plans with your passengers, including what to do in case of a man overboard, fire, or medical emergency.
- First Aid Training: Take a first aid and CPR course to be prepared for medical emergencies.
- Communication Devices: Equip your boat with reliable communication devices, such as VHF radios, and know how to use them.
Importance of Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies can save lives. Regular drills and keeping emergency contact information readily available ensure that everyone on board knows what to do in a crisis, reducing panic and improving response times.
Conclusion
Boating can be a safe and enjoyable activity if proper precautions are taken. Understanding the primary causes of boating fatalities and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Always prioritize safety. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a safer and more enjoyable boating experience for everyone on board.
By focusing on these essential safety measures and continually educating yourself and others, you contribute to a safer boating community. Remember, the responsibility of safety lies with each boater, and through collective efforts, we can reduce the number of boating fatalities and make our waters safer for all. Happy and safe boating!